Dr. V.K. Maheshwari, Former Principal
K.L.D.A.V(P.G) College, Roorkee, India
With special reference to Herbartian approach
A teacher who is attempting to teach without inspiring the pupil with a desire to learn is hammering on a cold iron.
Horace Mann
Teaching is a complex activity. it needs proper preparation and planning. lesson plan is the blue print of those teaching activities that are to be done in the class-room. Every teacher tries to plan the content in his own style so that he can teach systematically and effectively at the right moment.
MEANING AND IMPORTANCE OF LESSON PLANNING
Teaching is a process which involves those teaching activities which a teacher performs in the class-room. It is based on planning and specifically lesson planning. Thus, a lesson plan is a detailed plan prepared by the teacher in advance for the daily teaching. It helps the teacher in systematic, and effective teaching.
Lesson plan is a teaching outline of the important point of a lesson arranged in order in which they are to be presented; It may include objectives, points to be made, questions to be asked, reference to materials, assignments etc..
Lesson planning is a special skill that is learned in much the same way as other skills.. When the teacher is able to create his own lesson plans, it means he has taken a giant step toward “owning” the content the teach and the methods he use, and that is a good thing. Acquiring this skill is far more valuable than being able to use lesson plans developed by others. It takes thinking and practice to hone this skill, and it won’t happen overnight, but it is a skill that will help to define one as a teacher. Knowing “how to” is far more important than knowing “about” when it comes to lesson plans, and is one of the important markers along the way to becoming a professional teacher. It is also in keeping with a central theme of this site that one should learn to plan lessons in more than one way. The corollary is, of course, that there is no one “best way” to plan lessons. Regardless of the form or template, there are fundamental components of all lesson plans that one should learn to write, revise, and improve. The old adage, “Practice doesn’t make perfect; perfect practice makes perfect” is at the core of learning this skill. .
The teacher regularly achieves the teaching objectives and processes in the form of lesson planning.. It develops the possibilities of adjustment in the class-room situations which makes the teaching effective.It helps in recalling every step of curriculum unit
It also help in planning the process of teaching on the basis of class control, motivation and individual differences .Lesson plan is;
- Based on Previous Knowledge. As the teacher presents new knowledge on the basis of previous knowledge of the pupils, the lesson plan enables the pupils to gain knowledge conveniently while the teacher succeeds in acquiring his objectives.
- Psychological Teaching. In preparing lesson plans, the teacher uses teaching strategies, techniques, tactics and instruments keeping in mind the interests, aptitudes needs capacities and abilities of the pupils . This makes teaching more psychological.
- Suitable Environment. Objectives are fixed and the teaching strategies, tactics, techniques and material aid etc. are decided before hand in a lesson plan. This creates interest of the pupils in the lesson. It helps in creating proper environment. Teaching task goes in a very planned way.
- Determination of Activities. Activities of the teacher and pupils are pre-decided in a lesson plan according to the class level. The teacher decided what he and his pupils aresuppose to do in the class. This makes the teaching activities meaningful an purposeful. Both the pupil and the teacher become active in developing the lesson.
- Preparation of Material Aids. While preparing a lesson-plan, the teacher decides strategies, tactics, techniques instruments and aids to be used. He prepares the necessary and effective aids before starting the teaching task.
- Limitation of Subject-Matter. Limited subject-matter enables the teacher to give up irrelevant material. As he remembers only definite and limited matter its presentation becomes easy.
- Management of Teaching-Learning. Davis has rightly said “Lesson must be prepared as there is nothing so fatal to a teacher’s progress as unpreparedness”. A lesson-plan is the concept of management of teaching-learning. The teaching objectives are successfully achieved by making the teaching impressive. A well organized lesson-plan occupiesan important place in the success of teaching.
- Orderliness and Development in Thinking. Lesson plan creates orderliness and development in the thinking of the pupils enabling the teacher to achieve the teaching objectives while presenting the contents in an orderly way.
- Use of Theoretical Knowledge in Teaching. Theoretical knowledge attained by pupil teachers during their training period, is applied in the class with the help of lesson-plan. It helps in providing practical shape to the theoretical knowledge.
- Means for developing Teaching Skills. The lesson plan acts as an important means for developing teaching skill in the pupil teachers.
- Discipline in the Class. By preparing lesson plan, the teacher is aware of what, when and how much is to be done in the class. He absorbs all the pupils in their respective tasks. it results in appreciable class-room discipline.
- Evaluation Possible. A lesson plan has the provision of the evaluation, which makes the teacher aware of how his teaching has affected the pupils. It also evaluates the strategies, tactics techniques and aids used by the teacher and he can modify them accordingly.
- Teaching with Confidence. The preparation of a lesson plan makes the subject of teaching more clear to the teacher. This arouses self-confidence in him. Now he presents the new knowledge to the pupils with more enthusiasm and pleasure. This make the class lively.
- Revision of Knowledge. The teacher writes summary of the lesson, the reading of which helps pupils in the revision of the lesson.
- Economy of Energy and Time. By preparation of lesson plan the teacher can present the new knowledge in a proper sequence before the pupils and can successfully remove their doubts
TYPES OF LESSON PLANS
Based on the B.S.Bloom taxonomy of Educational objectives ,lesson plans can be classified in the following types;
Knowledge Lesson. Here the learner’s cognitive aspect of his mental activity is more active which result an increase in his knowledge. Knowledge lesson are those which cause an increase in the knowledge of various facts and events through the knowledge lesson such as the lessons of History, Geography, Economics, Civics, Mathematics, Science and Grammar.
Appreciation Lesson. These are based on the affective aspect of learner’s activity. These give aesthetic inspiration to the pupils and develop their appreciation. They take interest in studying these lessons. Poetry lessons are good example of this type.
Skill Lesson. In skill lessons, the psycho-motor aspect of the learner’s mental activity is more active. Skill lessons make the pupils efficient in doing some task, while the teacher provides some guidance to the pupils in the beginning. Following the teacher’s or guidelines all the pupils get involved in accomplishing the task. This provides man opportunities for experimenting and practice. The creative power of the pupils is more active in skill lessons. Painting, handicraft, gardening and agriculture etc. are examples of skill lesson.
CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL LESSON PLAN
Good lesson plans do not ensure students will learn what is intended, but they certainly contribute to it. Think of a lesson plan as a way of communicating, and without doubt, effective communication skills are fundamental to all teaching. Lesson plans also help new or inexperienced teachers in organizing content, materials, and methods. Developing own lesson plans also helps one “own” the subject matter content one is teaching, and that is central to everything good teachers do.
Psychological Base of the Lesson Plan is Gestalt learning theory of the Psychology. It follows the maxim of ‘whole to part’ teaching. It is considered that these units (parts) help in the understanding of the whole concept.
Teachers create lesson plans to communicate their instructional activities regarding specific subject-matter, effective lesson plans communicate, ineffective ones don’t. Almost all lesson plans developed by teachers contain student learning objectives, instructional procedures, the required materials, and some written description of how the students will be evaluated. Many experienced teachers often reduce lesson plans to a mental map or short outline. New teachers, however, usually find detailed lesson plans to be indispensable.
An ideal lesson plan should be-
- Divided into Units. All the relevant steps of (i) knowledge lessons (ii) skill lesson. (iii) Appreciation lessons should find a place in an ideal lesson plan. Each lesson should be divided into suitable units so that the pupils may understand them gradually.
- Objective based. It must be based on one or the other objective. Objective should be written and define clearly.
- Contain appropriate teaching aids. Correct decision regarding the charts, graphs, pictures, diagrams and maps should be taken. These should be marked at proper place, which a teacher issuppose to use while teaching.
- Based on Previous Knowledge. To avoid any difficulty in acquiring new knowledge by the pupils, an ideal lesson plan should be based on their previous knowledge.
- Simplicity of Language. The simplicity of the lesson plan and clarity of thoughts should be according to the mental level of the pupils. The lesson plan should be subject-oriented, not language-oriented.
- Time-sense. An ideal lesson plan is prepared according to the mental level of the pupil and the duration of periods. The adequate time should be assigned for every teaching step ..
- Use of Black-board. The black-board summary of each and every unit is written on the black-board immediately after teaching in small but complete sentences.
- Use of Illustrations. Examples are used having relevance with the daily life of the pupils. This depends upon the comprehensive knowledge and experience of the teacher.
- Individual Guidance. The technique and occasion of providing individual guidance to the pupils is indicated .
- Use of Strategies, Tactics, Techniques . To use appropriate strategies or methods, tactics, techniques and aids in order to classify the events and facts which occur in different situations the teacher has to gain the knowledge of maxims of teaching and general principles of teaching.
- Correlation. A possible correlation occurs to enable the pupils to acquire the knowledge as a whole.
- Teaching from Memory level to Reflective Level. Developmental and thought provoking question are asked in an effort to stretch the teaching from memory level to the reflective level.
- Determination of Activities. An ideal lesson plan should make clear what activities a teacher and the pupils are suppose to perform. They should be determined before-hand in an ideal lesson plan.
- Evaluation. There is a mention of the method of knowing the influence on the pupils. This involves evaluation of the methods used by the teacher.
- Home Work. There is a provision of home work to enable the pupils to learn the application of the acquired knowledge.
ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS IN PREPARING LESSON PLAN
- According to Bining and Bining “Daily lesson planning involves defining the objective, selecting and arranging the subject matter and determining the method and procedure.”
The following flow chart provides a bird’s eye view of the entire planning procedures-
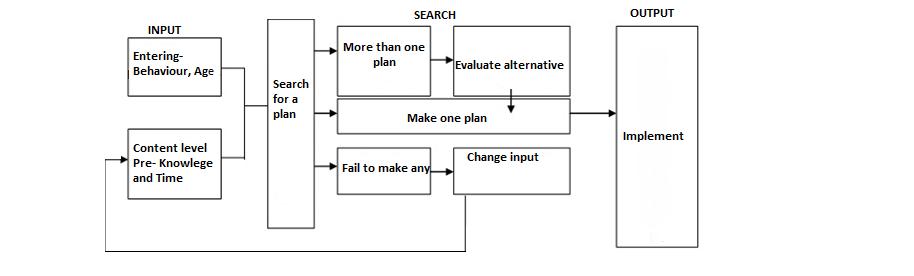 As shown above an ideal lesson plan must have the following essential elements;
As shown above an ideal lesson plan must have the following essential elements;
- Knowledge of Student’s Entering behavior-. The teaching method will be advantageous only when the nature of the pupils is known along with knowledge of the subject matter.
- Knowledge of the Subject. The teacher should know his subject well. If he has no clarity about his subject he will fail to clarify various facts and events of the lesson. He should read the whole lesson plan which he has prepared. He should not read the text-book only, but also read other supplementary books and the available material concerning the topic.
- General Knowledge of other related Subjects. The pupil teacher should possess general knowledge of all the subjects, because the knowledge is a complete unit and it cannot be divided into different water tight compartments;.
- Clarity of Objectives. There should be clarity of objectives to make the both pupils and the teachers active to achieve them.
- Division in Units. While preparing the lesson plan, the teacher should divide the topic in units. this simplifies the preparation of the lesson plan. it is acquired easily by both the pupils and the teachers.
- Flexibility. The lesson plan is a slave not the master of the teacher. Hence, the teacher is free to make changes in the lesson plan in order to create attraction and interest in the lesson.
- Knowledge of the Principles and Strategies of Teaching. The teacher must know the principles of teaching, maxims of teaching, teaching methods and techniques so that he may use the teaching methods and techniques in the lesson plan.
- Time duration Sense. The teacher should have time sense. He should clearly know how much time he will take to present the lesson before the pupils and how many activities can be performed in the prescribed durations.
- Clarity about Previous Knowledge. While preparing the lesson plan, the teacher should know the previous knowledge of the pupils because the new knowledge imparted on the basis of previous knowledge is easily stabilized.
- Knowledge of Class Level. He should know the class-level for which he is to prepare the lesson plan.
- Use of Instructional material . While preparing the lesson plan the teacher should decide at what step the material aid is to be used and what is to be clarified with that aid. This maintains the neutrality and interesting feature of the lesson plan.
HERBARTIAN APPROACH OF LESSON PLANNING
John Fredric Herbart was a great European educationist and philosopher of 19th century he advocated that teaching should be planned actively if we intend to make it efficient He applied the knowledge of psychology regarding the Learning process.
Herbartian approach is based on apperceptive mass theory of learning. The main thing in that theory is that the learner is like a clean slate and all the knowledge is given to him from outside. If new knowledge is imparted by linking with old knowledge of the student it is acquired easily and is retained for a longer period. The contents should be presented into units and those units should be arranged in a logical sequence.
Based upon Educational psychology Herbart’s educational ideology advocated the following four elements for a successful teaching.
- Interest. The teaching process should be interesting. When the interest of pupils is crated in some subject, their attention is attracted towards it. They acquire the new knowledge very easily.
- Apperception. The entire knowledge is provided to the pupils from outside. Apperception of this external knowledge occurs in the unconscious mind of the pupils. By relating new knowledge to the previous knowledge of the pupils, their learning is simplified. Hence, in order to make the learning process effective, the teacher should move from known to unknown.
- General Method. Learning activity occurs in a definite sequence. Hence, the activities of the unit should be edited in a definite sequence and in a logical order.
- Correlation. Knowledge is one unit. All the subjects should be studied after correlating each other in the form of one unit. All the subject of the curriculum should be taught by correlating them with History.
Steps of Teaching Approach
- Clarity. The teacher should present the subject-matter with clarity. The subject-matter to be taught is broken into various facts so that pupils pay attention to each fact or element.
- Association. The new knowledge of the pupils is related to their previous knowledge.
- System. New knowledge or thought should be organized in sequence on the basis of logic. The specific are separated from the generals which may enable the pupils to view the mutual relations between various fact or elements so that they may gain the knowledge of ‘whole’.
- Method. The pupils apply the gained knowledge to the new situations.
HERBARTIAN FIVE STEPS TEACHING
While Herbart emphasized only four steps his followers modified the above four steps. Ziller , a disciple of Herbart, divided the first step i.e., clarity into two introduction and presentation. Ryan incorporated one more step termed as ‘Statement of Aim’ in between these two. Still other disciples of Herbart changed the names of other three steps. The term comparison was used in place of association, generalization in place of system and application in place of method. Thus, resulted five steps in place of four. These five steps are termed as Herbartian five steps of teaching.
Preparation/ Introduction-. Some question are asked from the pupils in order to test their previous knowledge so that curiosity may arouse in them for learning of new knowledge. By testing their previous experiences the pupils are prepared for acquiring new knowledge.
-
- Statement of Aim
- Presentation. The lesson is developed with the cooperation of the pupils. Opportunities are provided to pupils to learn themselves by stimulating their mental activity. The teacher tries to receive most of the points from the pupils by questioning so that the new knowledge may get related to the previous knowledge.
- Comparison and Association-. In this, the facts, events and application taught are related mutually by comparison to enable the pupils to understand the taught material. The teacher establishes a relationship between two subjects and also between the facts and events of one subject and the facts and events of the other subject. He compares them so that the new knowledge may get stabilized and clarified in the minds of the pupils.
- Generalization-. Herbart termed this step as ‘system’ After explaining the main lesson, the pupils are provided with opportunities to think. They formulate such principles and rules which may be used in various situations of the future life.
- Application-. In Application it is observed whether the acquired knowledge may be applied to the new situations. The teacher verifies this by asking recapitulate questions or by providing opportunities to apply the acquired knowledge in the new saturations. This stabilizes the new knowledge and validity of the rules may also be proved.
-. Here, the topic becomes clear to the pupils and the teacher himself is supposed to write the topic on the black-board in clear words.
HERBARTIAN LESSON PLAN MODEL
Date………. Class…………… Period………………..
Subject………………. Topic………………
- 1. General Objectives. These objectives are formulated by the teacher in his subject keeping in view the entering behaviors of the learners. For example: 1. To develop the knowledge of grammar among the students…
- Specific Objective. These objectives are formulated on the basis of general objectives and considering the nature of the topic and level of students. These are specified in terms of knowledge, skill or appreciation. These objectives are written in behavioral terms. For Example: (i) Students will be able to recall the definition of noun. (ii) Students will be able to enumerate the examples of noun….
- Introduction. Here, the teacher employs his insight and experiences for liking new knowledge with the previous knowledge of the students. The topic is not introduced directly but it is usually emitted by the student’s responses by asking introductory questions.
- Teaching Aids. Audio-visual aids are selected according to the proposed topic.
- Previous knowledge. Students’ previous knowledge is mentioned. For example: Students are familiar with figure of speech. They know that nouns are naming words.
- Statement of Aim. The teacher gives his statement of teaching topic by incorporating the student’s responses. For Example: “Today, we will study about the noun and its kinds.”
- Presentation. The teacher prepares the developing questions after introducing the topic. The question are arranged in logical sequence, i.e., from simple to complex, considering the structure of the topic.
- Explanation. The teacher is supposed to explain the answers of the given developing question. as whole of the content-matter is in the question-answer form.
- Black –board Summary. The teacher has to prepare the black-board summary of his teaching point and explanations.
- Review Questions. The purpose of these questions is to practice the student’s learning and to evaluate their performance whether they have comprehended the teaching unit or not. These review questions are asked only after rubbing the black-board summary. For example: Q.1. What is the definition of ‘Noun’? Q.2. Give some examples of Noun…..
- Home assignments. At the end of the lesson plan, home assignment is given to the students on the same teaching unit. The purpose of home work is to practice, to organize and to study the topic for better understanding and retention.
Advantages
- Organized Teaching. Each step has been organized in a logical order which provides an opportunity to the fresh teacher to become aware of future mistakes. Originality is never affected and the teaching goes on in a very organized way.
- Acquiring thoughts as apperception . Herbart believed that when the new thought related to the thoughts lying in unconscious mind of the pupils are presented, the thoughts of unconscious mind come to the conscious mind, establish relationship with the new thought and again go to the unconscious mind. Herbart termed this material process of acquiring thoughts as apperception.
- Use of Inductive and Deductive Methods. While presenting the new knowledge, help of various examples is sought through ‘generalization’ and rules are derived. it is an inductive method. In the step application, these rules are to be executed, this is a deductive method. Thus, both indicative and deductive methods are used in this five steps approach.
- Recapitulation. Such question are asked while recapitulating which, on answering, result in the learning and application of the acquired knowledge in new situations.
- Correlation Possible. Herbart considered entire knowledge as a single unit. The knowledge of the pupils is acquired in a single unit. This allows to establish a correlation between previous and new knowledge and between all subject of the curriculum.
Limitations
- Mechanical Method of Teaching. The use of the these steps takes away the freedom of the teacher as he cannot incorporate his independent thought in any step. This reduces his originality. Hence, Herbartian approach is a mechanical method of teaching.
- No Place for Individual Differences. While using Herbartian approach. Similar questions are asked to the entire . This overlooks individual differences.
- Useful in Knowledge Lesson only. Herbartian approach is useful in the knowledge lesson only, not in appreciation and skill lessons.
- Teacher More Active. In Herbartian approach, the teacher has to be more active. It is more desirable if the pupils remain more active than the teachers. As this teaching method is not activity-centered, pupils don’t’ get any motivation for learning.
- No need of Generalization. Generalization is not needed while teaching language, geography, history, music and arts etc. Thus, all the five steps are not needed while teaching.
- Uninteresting. This approach stresses upon the teaching of all the subjects of curriculum in a similar sequence overlooking the interests, attitudes, abilities, and capacities of the pupils according to their mental development. The entire teaching become monotonous. The pupil does not show any interest in acquiring new knowledge . Thus, Herbart’s teaching method is not interesting
- Difficulty of Correlation. Considering the knowledge as a complete unit, Herbart emphasized correlation between different subjects for the unity in the mental life of the pupils, But following these five steps teachers impart the knowledge of different subjects to the pupils differently. They seek to establish a correlation between various subjects in order to bring integration in the mental life of the pupils which is essentially difficult, if not impossible.
So in nutshell it can be concluded that Herbartain Five-Step Approach, is an impressive and psychological teaching method. It includes both inductive and deductive methods. A correlation among all the subjects of the curriculum is possible by its use. There is a provision of recapitulation in the step under ‘application’. However, some educationists point out that this method is useful only for knowledge lessons. Generalization is not needed in every lesson. Herbart’s method is mechanical. There is no place for individual differences. It does not motivate the pupils to learn by doing. The correlation between the different subjects is essentially difficult. Glower points out that in Herbartian approach; emphasis is laid on teaching only instead of learning. This reduces the freedom of the teacher. Pupils also become passive. Neither is their character formed nor do they reach their desired goals. However, the pupils-teachers should follow this approach with necessary changes keeping its merits in view.
Acknowledgement
To Arunima Maheshwari for being the scribe of this article.


your website is soo good. i wish i could write like you someday. thanks for the good post.http://www.frasesparacelular.com